class ii malocclusion division 2
An individual case is illustrated. Angle and subsequent authors differentiated between Class II division 1 and 2 malocclusions based on the position of the incisors.
Permanent first molar or the entire width of a premolar.

. Upper central incisor are retroclined overjet is usually minimal but may be increased. D Class 111 malocclusion. Prospective cohort studies of treatment for II2M 3438One study followed Class II Division 2 malocclusion patients treated with functional appliance therapy preceded in some patients by a removable appliance to procline the maxillary incisors.
1 Many treatment options are available for the correction of Class II malocclusion depending on what part of the. The discrepancy between the upper and lower teeth does not match the discrepancy between the upper and lower teeth where the molars and canines are located red and blue arrows. A Class II division 2 II2 relationship.
However lip cheek and tongue pressures that are associated with the environmental effect are considered to have an effect. Class II Division 1. Incisor relationships are unique.
This is a systematic review conducted according to the PRISMA statement. Class II Division 2 malocclusions often have skeletal patterns more nearly approaching Class I than Class II Division I. The Angles class II malocclusion is associated with two major factors skeletal.
A method of planning and treatment. The restorative result can be disastrous if the pitfalls associated with a lack of thorough evaluation are not recognized and correctly addressed in the treatment plan. The Cochrane Oral Health Trials Register the Cochrane Central Register of.
Class II division 2 malocclusion. Teeth are proclaimed and a large overjet is present. Proclination of upper incisors andor retroinclination of the lower incisors by a habit or the soft tissues can result in an increased overjet in any type of skeletal pattern In class II division 1 the lips of the parents are usually incompetent and they try to compensate it via circumoral muscular activity rolling the lower lip behind the upper.
Treatment problems related to this malocclusion require that the clinician pay particular attention to the vertical dimension. Where the upper incisor lie outside the control of. Although Angle classified the malocclusion in 1890s there is still lack of clarity regarding the pathognomonic features of Class II division 2 malocclusion.
INTRODUCTION Many treatment approaches are currently available to the orthodontist for altering the occlusion relationship typically found in class- II division-2 malocclusion. Class IIdivision 2 malocclusion. The Class II division 2 malocclusion occurs the least often and obtaining the sample for the purpose of evaluation has always remained a critical issue.
The method combines improvement in dental facial aesthetics with reduction in overbite and inter-incisor angle. C Class II division 2 malocclusion. The molar relationships are like that of Class II and the maxillary anterior teeth are protruded.
A classe II div 2 malocclusion has typically retroclined maxillary incisors. Mild Class II skeletal pattern Upper incisors usually lie outside the control of the lower lip resulting in a Class II division 1 But where the lower lip line is high relative to. The case report supports the hypothesis that heredity is not the sole controlling factor in the etiology of Class II Division 2 malocclusion.
Were in Class II relation biiaterallyFig1. Class II division 1. Also the prevalence of mandibular movement pattern.
The principal findings are an essentially normal skeletal pattern outside the immediate dental region with the major deviations directly involving the dentition. The aim of this study was to evaluate the relation between perioral pressures and the upper incisor inclination in CII2 malocclusion. The Class II Division 2 dental malocclusion with the classic retro-inclination of the upper incisors can be one of the most difficult restorative challenges faced in practice.
This paper presents a method of cephalometric treatment planning for class II division 2 malocclusions. The class II division 2 differs from division 1 by the following characteristic. Our objectives were to evaluate the evidence with regard to the effectiveness and stability of orthodontic treatment interventions for Class II Division 2 malocclusion in children and adolescents.
The lower incisor edges occlude on or lie below the cingulum plateau of the upper incisiors. Persons with class II division 2 malocclusion are characterized by a very specific dento-skeletal and soft-tissue profile a profile in which a protruding nose and chin retruding lips concave and shortened lower third of the face and gummy smile are dominant which is the opposite of the currently modern profiles convex profile of protruding lips and small chin. 34 A distal path of closure was found in 50 of the Class II Division 2 malocclusion sample before treatment and.
The etiology of Class II division 2 CII2 malocclusion focuses on heredity. Papadopoulos in Orthodontic Treatment of the Class II Noncompliant Patient 2006 Introduction. British Journal of Orthodontics 231 pp29-36.
Class II malocclusion includes those anomalies with the mesiobuccal cusp of maxillary first permanent molar occludes mesial to the mesiobuccal grove of the mandibular first permanent molar. Class II malocclusion is one of the most common problems in orthodontics with an estimated one-third of all orthodontic patients treated for this condition. A morphologic and functional evaluation of Class II division 2 malocclusion based on digitized data from cephalometric and cinefluorographic radiography and dental casts.
Where the lower lip line is high relative to the upper incisors a class 11 division 2 can result. Commonly associated with a mild class 11 skeletal pattern. The mesio buccal cusp of the maxillary first permanent molar occludes in the space between the mesiobuccal cusp of the mandibular permanent first molar and the distal aspect of the buccal cusp of the second pre molar.
A pair of monozygotic twins with different malocclusion phenotypes Class II Division 2 and Class II Division 1 is presented. The condition is characterized by distal position of the lower jaw as compared to the upper jaw. Angles class II malocclusion is type of orthodontic problem that indicates abnormalities in the tooth positioning as defined by Edward Angle.
A Class II malocclusion is present when the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar occludes mesial to the mid buccal groove of the mandibular first molar. Examples of the applications commonly used being shown in the treatment of an adolescent patient. Class II Malocclusion has 2 subtypes to describe the position of anterior teeth.
These treatments include a variety of extra- oral traction.

Dentaltown Where The Dental Community Lives Dental Hygiene School Dental Hygiene Student Dental Assistant Study

Orthodontics Mcq Orthodontics Panoramic Radiograph Supernumerary Teeth

Class Ii Division 2 Malocclusion In Orthodontics Orthodontics Facial Esthetics Orthodontic Treatment

Orthodontist In Pune Braces Cost In Pune Dentist For Invisalign Invisible Braces Orthodontist Braces Cost Tooth Extraction Care

Myofunctional Appliances Activator I Appliances Dental Student Appliances Design

Pin By Neha On Orthodontics In 2022 Orthodontics

Pin By Sarina Knight On Anatomy Dental Anatomy Dental Hygiene School Nerve Anatomy

Overbite Intruding Lower Youtube Lower The Creator
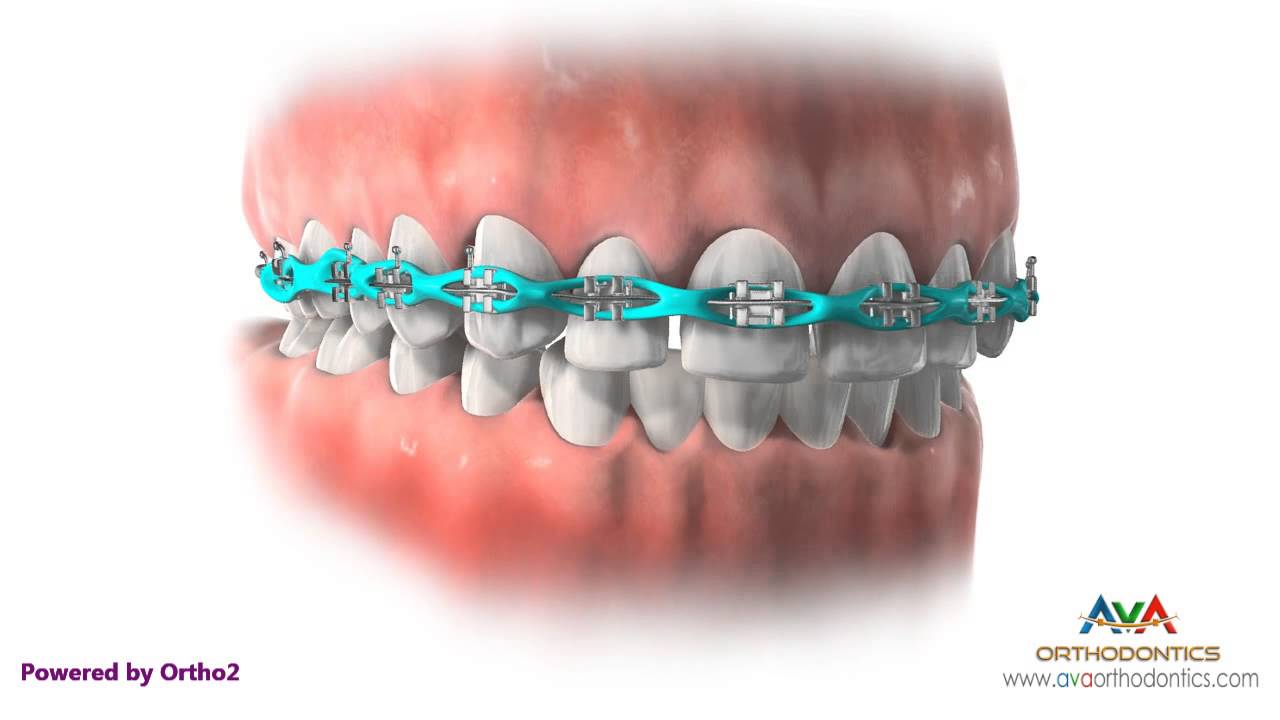
Space Closure By Power Chain Orthodontic Treatment Orthodontic Treatment Orthodontics Chain

978 620 2 79766 5 In 2021 Orthodontics Dental Health Dentistry

Midline Correction Elastic Youtube Dental Braces Orthodontics Braces Treatment

Dentaltown Where The Dental Community Lives Orthodontics Dental Dental Hygiene School

Pin By Sathya Kumaresan On Neet Orthodontics Orthodontics Muscle Science

Orthodontics Dental Dental Hygiene School

Cc457 Chris Top 11 Cases 5 Crowded Cii Division 2 Malocclusion Youtube Esthetics Crowd Dental



